Reflection of Light
Reflection of Light: Overview
This topic covers concepts, such as Reflection of Light, Laws of Reflection of Light, Properties of Image in Plane Mirror, Beam of Light, Normal Incident Rays and Grazing Incident Rays.
Important Questions on Reflection of Light
Assertion(A): The formula connecting and for a spherical mirror is valid in all situations for all spherical mirrors for all positions of the object.
Reason (R): Laws of reflection are strictly valid for plane surfaces.
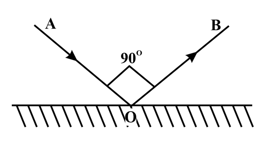
In the figure given, AO and OB are the incident and reflected rays respectively. . Then the values of angle of incidence and angle of reflection are .
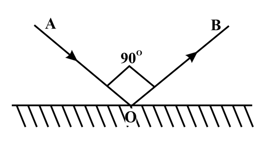
In the figure given, AO and OB are the incident and reflected rays respectively. .What is the angle of incidence and angle of reflection in degrees in this case?
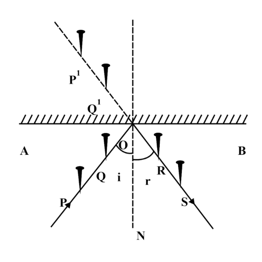
The incident ray passes through P and Q. The reflected ray passes through R and S. Incident ray and reflected ray lies on the plane of _____.
The radius of curvature of a plane mirror is infinity.
Angle of _____ is always equal to the angle of reflection.
This is the angle (in degree) of reflection when a ray of light falls normally on a plane mirror.
The height of an object placed in front of a plane mirror is . The height of the virtual image formed is _____ .
An object is placed in front of a plane mirror. The distance between the object and its virtual image is _____ .
The image formed by a plane mirror is:
A ray of light falls on a plane mirror at an angle . What is the angle between the surface and reflected ray.
Keep two mirrors as shown in the picture and place a small candle in the centre. How many images can you see in both the mirrors?

A man stands in front of a large plane mirror. How far must he walk (in meters) before he is away from his image?
A ray of light takes grazing incidence on the first face of a prism and the emergent ray is normal to the second face of the prism. If is angle of deviation then the refracting angle of the prism is equal to
Grazing angle is also represented as:
A group of light rays is known as a_____of light.
If we stand before a plane mirror and move our right hand, our image appears to move its left hand. In fact, our entire image is reserved sideways. This sideways reversal of the image is known as _____.
An object of size is placed at in front of a concave mirror of focal length . At what distance from the mirror should a screen be placed so that a sharply focussed image can be obtained? Find the image size.
_____ (Angle of incidence/ Angle of reflection) is the angle made by the incident ray with the normal to the surface at the point of incidence.
A concave mirror produces three times enlarged image of an object placed at 10 cm in front of it. Calculate the focal length of the mirror.
